Complete Statutory Compliances checklist (2025 Updated)
Introduction
In today’s regulatory-driven business environment, compliance is non-negotiable. Statutory compliance refers to the mandatory legal framework set forth by government agencies to govern and guide various business functions and obligations, ensuring that companies adhere to policies that protect both employees and employers. Regardless of the industry or business size, meeting these requirements is essential to avoid legal repercussions and enhance organizational efficiency.
Understanding Statutory Compliance
Statutory compliance encompasses the body of regulations that businesses are legally required to follow. It covers a wide range of areas, including employment laws, wage and tax obligations, safety regulations, and other policies mandated by the government to maintain an ethical and balanced work environment. Failing to meet these obligations can lead to penalties, legal challenges, and damage to the company’s reputation.
Statutory compliance laws are dynamic and may evolve based on political, social, and economic changes, meaning that organizations must be vigilant in regularly updating their policies. Compliance requirements not only serve to keep businesses aligned with the law but also help foster transparency, ethical behavior, and employee well-being, which are essential for long-term success.
Advantages of Adhering to Statutory Compliance
For companies, following statutory compliance has several notable benefits. Here are some of the primary reasons compliance should be a priority for every business:
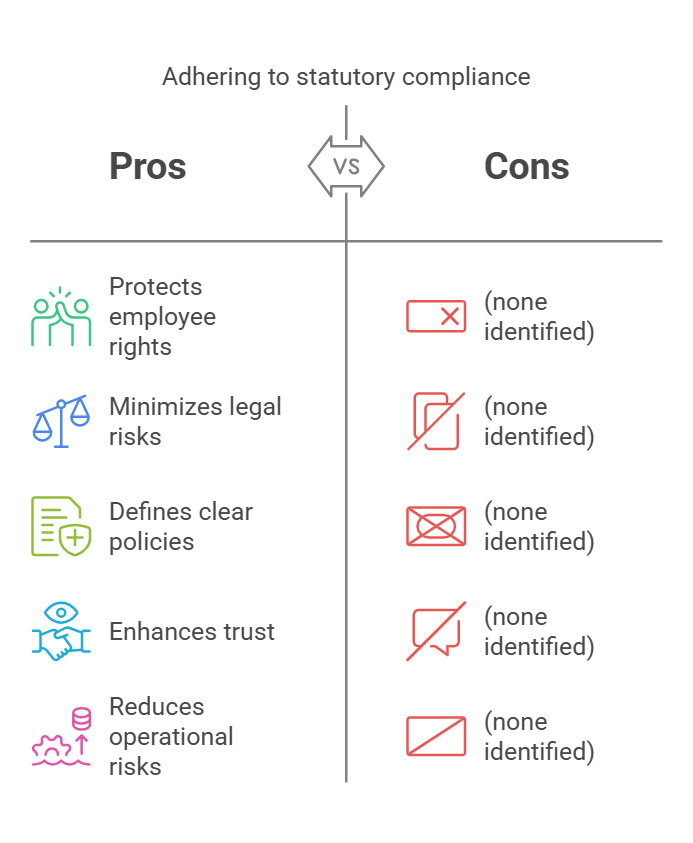
1. Protecting Employee Rights and Safety
One of the core objectives of statutory compliance is to protect the rights of employees and provide a secure working environment. By adhering to regulations related to fair wages, work hours, health and safety, and benefits, businesses can ensure that employees are treated fairly and feel valued.
2. Minimizing Legal Risks and Penalties
Compliance requirements help organizations avoid legal issues by establishing a framework that prevents common legal pitfalls. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties, from fines to suspension of business activities. Meeting these obligations helps companies reduce their exposure to financial and reputational risks.
3. Defining Clear Company Policies
Statutory regulations guide the development of internal company policies and procedures, ensuring they align with government standards. This framework helps companies establish fair employment practices, wage distribution, safety protocols, and employee benefits, leading to a more transparent and efficient work environment.
4. Enhancing Public and Employee Trust
Organizations that adhere to compliance laws are seen as trustworthy and credible by the public, employees, and investors alike. Compliance demonstrates the company’s commitment to ethical practices, which fosters a positive reputation and strengthens relationships with stakeholders.
5. Reducing Operational and Strategic Risks
While compliance cannot eliminate all business risks, it plays a key role in mitigating legal and financial risks. Adherence to statutory requirements enables businesses to prevent certain challenges, such as workplace disputes, employee grievances, and litigation, helping ensure smooth operations.
Detailed Statutory Compliance Checklist for 2023
Below is a comprehensive list of essential statutory compliance requirements that all organizations need to follow to ensure lawful operations:
1. Shops And Commercial Establishments Act
The Shops and Commercial Establishments Act outlines essential guidelines for businesses, specifically retail outlets and other commercial establishments. It sets standards for working hours, payment schedules, leave entitlements, and holidays. This Act is critical to safeguarding the rights of employees working in commercial settings.
2. Employees’ Provident Funds and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952
The Employees’ Provident Fund (EPF) Act mandates that employers contribute to an employee’s provident fund, ensuring long-term savings for employees. This fund provides financial security and benefits in cases of retirement, illness, or other emergencies, underscoring the importance of social security in the workforce.
3. Employees’ State Insurance Act, 1948
The Employees’ State Insurance (ESI) Act provides a social safety net for employees, granting medical care and financial assistance in cases of health-related incidents. This is a joint contribution between the employer and employee, ensuring that workers have access to essential medical services.
4. Professional Tax Act, 1975
The Professional Tax Act is applicable to individuals earning an income, whether through employment or by practicing a profession (e.g., doctors, lawyers, accountants). It imposes a tax at a specified rate, which varies by state, on professionals to support government infrastructure and services.
5. Labour Welfare Fund Act, 1965
The Labour Welfare Fund Act is aimed at enhancing the working conditions and overall welfare of laborers. It covers aspects such as housing, medical care, and educational benefits for employees and their families, providing a better standard of living for workers across industries.
6. Contract Labour (Regulation & Abolition) Act, 1970
The Contract Labour Act regulates the employment of contract labor and prohibits their use in specific sectors. It ensures that contractors and companies provide fair working conditions, adequate safety measures, and timely wages to contract laborers, thereby reducing exploitation.
7. Child Labour (Prohibition & Regulation Act), 1986
The Child Labour Act strictly prohibits the employment of children in hazardous occupations and industries. This law regulates permissible occupations for minors, ensuring that children are protected from exploitation and dangerous work environments.
8. Minimum Wages Act, 1948
The Minimum Wages Act ensures that workers receive a minimum wage that covers basic living expenses. It prevents unfair wages and guarantees that workers are compensated appropriately based on their skills, experience, and job nature.
9. Payment of Wages Act, 1936
The Payment of Wages Act mandates the timely payment of wages and regulates deductions, protecting employees from unfair wage practices. By adhering to this law, companies promote financial transparency and trust.
10. Payment of Bonus Act, 1965
The Payment of Bonus Act requires companies to distribute annual bonuses based on employee performance and company profits. This not only motivates employees but also helps align individual goals with organizational success.
11. Maternity Benefit Act, 1961
The Maternity Benefit Act ensures that women employees receive maternity leave, medical benefits, and workplace support during pregnancy. It protects the rights of female workers and promotes work-life balance, allowing women to manage both personal and professional responsibilities.
12. Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972
The Payment of Gratuity Act provides gratuity as a form of retirement benefit for employees who have served a specific period with the organization. This Act secures the financial future of employees post-retirement.
13. Equal Remuneration Act, 1976
The Equal Remuneration Act is vital for promoting workplace gender equality by ensuring that men and women are compensated equally for performing similar work. This Act helps eliminate gender-based wage discrimination and promotes fairness.
14. Employment Exchange (Compulsory Notification of Vacancies) Act, 1959
The Employment Exchange Act mandates that certain employers notify government employment exchanges of vacancies, assisting in the placement of job seekers and reducing unemployment.
15. Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition & Redressal) Act, 2013
The Sexual Harassment Act requires companies to establish mechanisms to prevent and address instances of sexual harassment at the workplace, fostering a safe and respectful environment for all employees.
16. Employees’ Compensation Act, 1923
Formerly known as the Workers’s Compensation Act, this law provides compensation to employees or their families in cases of injury or accident at work. It helps relieve the financial burden on employees affected by work-related incidents.
17. Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) Act, 1946
The Industrial Employment Act requires companies to clearly define employment terms, policies, and procedures through standing orders. This clarity in employment terms fosters a more transparent and structured work environment.
18. Industrial Disputes Act, 1947
The Industrial Disputes Act provides a legal framework for resolving labor disputes, promoting peaceful negotiations, and preventing conflicts in the workplace. This Act covers procedures for conciliation, arbitration, and other dispute resolution methods.
19. Apprentices Act, 1961
The Apprentices Act regulates the engagement and training of apprentices across various industries, providing a formal structure for skill development. It allows apprentices to acquire job-relevant skills under supervised conditions.
20. Interstate Migrant Workmen (Regulation of Employment and Conditions of Services) Act, 1979
This Act protects interstate migrant workers, ensuring they are provided fair working conditions, housing, and timely wages. It reduces the exploitation of these workers, often employed in temporary or seasonal roles.
21. Factories Act, 1948
The Factories Act is pivotal for worker health, safety, and welfare within factory settings. It includes provisions related to safe working conditions, work hours, adequate ventilation, and emergency protocols, ensuring workers’ safety in potentially hazardous environments.
22. Trade Unions Act, 1926
The Trade Unions Act governs the formation, registration, and functioning of trade unions, allowing workers to organize and represent their rights and interests. Trade unions play a significant role in advocating for fair treatment and working conditions, making this Act critical for collective bargaining.
Conclusion
In 2024, statutory compliance is a cornerstone of business sustainability and integrity. By adhering to these comprehensive regulations, organizations can not only avoid legal repercussions but also foster a work environment that values employee rights, safety, and ethical practices. Compliance ensures the organization is equipped with the tools to manage risks, protect employee welfare, and maintain a reputable public image.
For businesses seeking a seamless approach to managing these requirements, Quikchex HRMS offers a robust compliance solution that simplifies the complexities of HR compliance. Quikchex provides automated updates on changing regulations, ensures accurate tracking of statutory obligations, and supports companies in maintaining alignment with the latest legal standards. Partnering with Quikchex HRMS ensures your business can stay compliant efficiently and confidently, securing a solid foundation for growth and operational excellence.